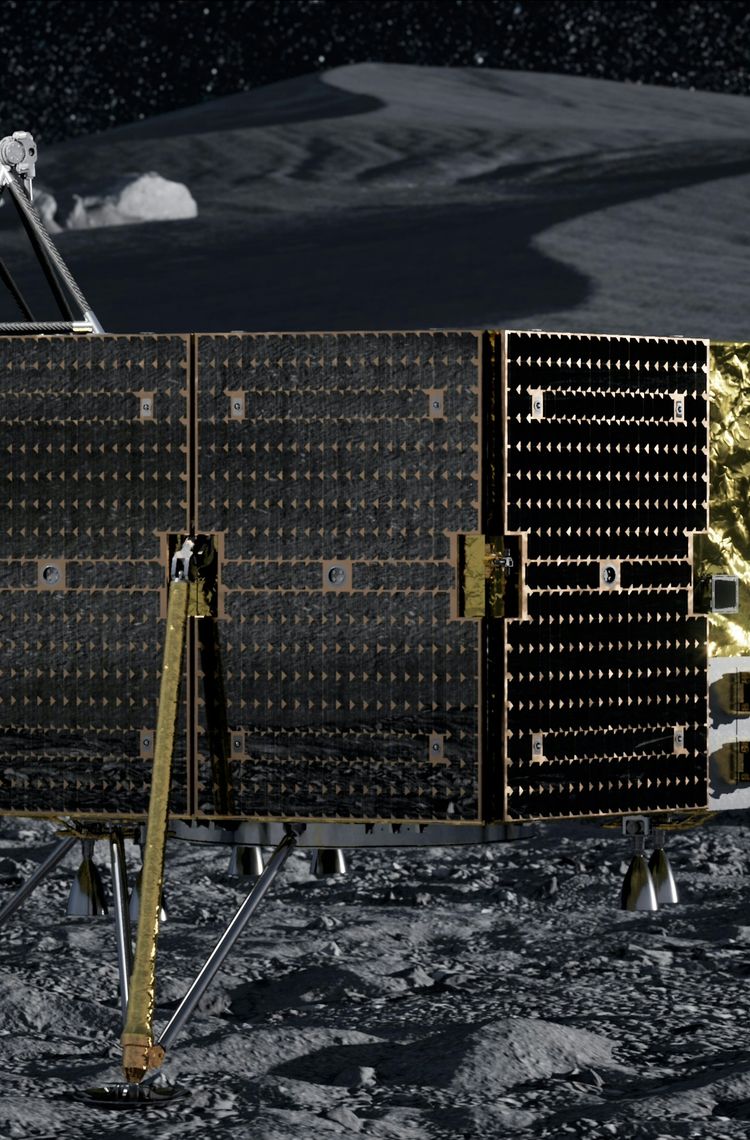
Off-the-shelf solar panel technology for small satellites selected by Masten for its XL-1 lunar lander
Leiden, the Netherlands, 20 July, 2021 – Today, Airbus announced that its Sparkwing solar panels were selected by USA-based Masten Space Systems for their XL-1 lunar lander. In 2023, the XL-1 spacecraft will land at the lunar South Pole as part of NASA’s Commercial Lunar Payload Services program. XL-1 will be equipped with six body-mounted Sparkwing solar panels, to be delivered next year, to charge the vehicle’s power system during transition to the Moon as well as during operations on the Moon’s surface.
The Sparkwing solar panels from Airbus are the world’s first commercially available off-the shelf option for small spacecraft. Plugging 3D models of standard Sparkwing components into the spacecraft design allowed for a speedy evaluation on where to place items and where it would need customization to meet the specific needs of Masten Mission 1. This led to a XL-1 specific design derivative of the Sparkwing catalogue product, with increased panel sizing and cut-outs on both long edges of the panel to accommodate the landing legs of the spacecraft. Each solar panel has 320 solar cells, with 3G30 space-grade solar cells provided by Azur Space. Building on over fifty years of experience in developing solar arrays, Airbus uses a “mix and match” approach of combining standard components with specific adaptations where needed for the Sparkwing solar panels.
“The Sparkwing team have been a delight to work with,” said Alison Dufresne, lunar engineering manager at Masten Space Systems. “They provide high quality end to end services including design, analysis and testing. With their previous experiences with missions like ExoMars, Rosetta and Galileo, we were confident that they were the right choice for our mission. Masten Mission 1 will be the first of many Masten missions to the Moon, Mars, and beyond.”
For Masten Mission 1, XL-1 will deliver payloads to the Moon’s South Pole to assess the composition of the lunar surface, detect volatiles such as water, methane, and carbon dioxide, and evaluate radiation in advance of human missions.
“Masten is working with us on this amazing mission with a pragmatic ‘get it done’ mindset. Our technology, which was originally developed for low-earth orbits, now finds its way to this lunar exploration mission”, said Marloes van Put, Sparkwing program manager at Airbus Defence and Space Netherlands.
@mastenspace @AirbusSpace #Sparkwing
Your media contacts
Contact us
Ralph Heinrich
AIRBUS | Defence and Space